应用程序启动流程
目录
启动流程简介
官方文档 App startup time给出了冷启动流程:
系统进程负责:
- Loading and launching the app.
- Displaying a blank starting window for the app immediately after launch.
- Creating the app process.
简单来说就是创建App进程。App进程被创建完成之后,完成以下任务:
- Creating the app object——创建Application对象。
- Launching the main thread.——启动主线程。
- Creating the main activity.——启动主Activity。
- Inflating views.——加载Views。
- Laying out the screen.——放置screen。
- Performing the initial draw.——执行最初的绘制。
应用程序冷启动重要环节示意图:(原图地址:https://developer.android.com/topic/performance/images/cold-launch.png)
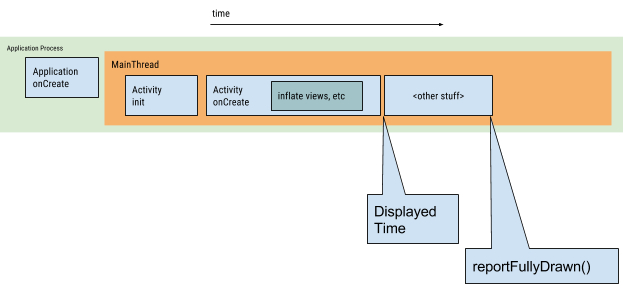
启动流程分析
创建App进程
App进程由其父进程zygote创建(fork)。通过adb shell ps可以查看进程树:
$ adb shell ps
USER PID PPID VSZ RSS WCHAN ADDR S NAME
root 1 0 16928 3204 0 0 S init
root 1692 1 1359724 130416 0 0 S zygote
u0_a43 4334 1692 1479728 105876 0 0 S com.android.calculator2
例如启动一个计算器应用,可以看到其对应的进程名为"com.android.calculator2",其父进程为zygote,zygote的父进程为init。系统开机之后,首先启动init进程,init进程会启动zygote进程,等等。进程树如下:
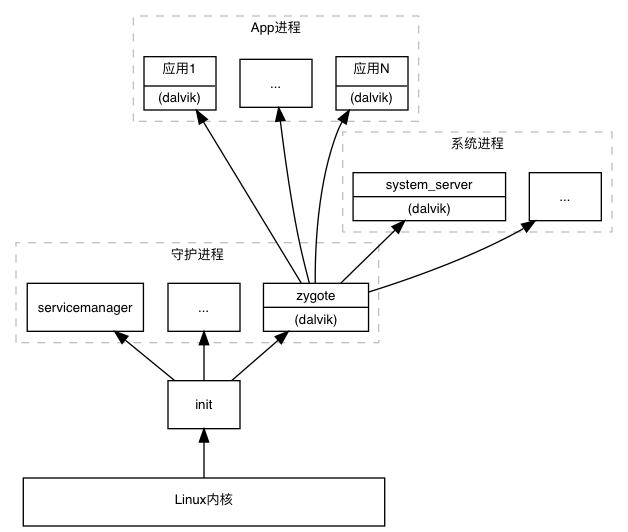
假定系统已经开机完成,正常展示系统桌面。此时点击桌面图标,从这里开始讨论应用程序的启动。ActivityManagerService首先请求zygote进程fork一个子进程,并指定进程主类为ActivityThread(entryPoint = "android.app.ActivityThread")。
fork完成之后,ActivityThread.main(String[] args)方法被执行:
/**
* This manages the execution of the main thread in an
* application process, scheduling and executing activities,
* broadcasts, and other operations on it as the activity
* manager requests.
*
* {@hide}
*/
public final class ActivityThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>");
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
Looper.loop();
}
}
刚创建时进程名还是"<pre-initialized>",顾名思义,预初始化。接下来这个进程通过thread.attach告诉ActivityManagerService已经创建成功,这里需要提一下,ActivityManagerService在请求zygote创建子进程之前会保存一个ProcessRecord对象,目的是当子进程创建出来之后知道该赋予其什么样的属性。
ActivityManagerService.java:
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,
int pid) {
// Find the application record that is being attached... either via
// the pid if we are running in multiple processes, or just pull the
// next app record if we are emulating process with anonymous threads.
ProcessRecord app;
if (pid != MY_PID && pid >= 0) {
synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {
app = mPidsSelfLocked.get(pid);
}
} else {
app = null;
}
thread.bindApplication(...);
//...
if (mStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked(app)) {
didSomething = true;
}
}
ActivityStackSupervisor.java:
boolean attachApplicationLocked(ProcessRecord app){
realStartActivityLocked(app);
}
final boolean realStartActivityLocked(app){
app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(intent);
}
thread.bindApplication通过Handler转主线程调用handleBindApplication方法,此时进程名正式改为应用包名:
private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) {
// send up app name; do this *before* waiting for debugger
Process.setArgV0(data.processName);
}
至此认为App进程创建完成。
启动主线程
ActivityThread.java
private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) {
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
Looper.loop();
}
创建Application对象
ActivityThread.java
private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) {
// packageInfo = new LoadedApk
data.info = getPackageInfoNoCheck(data.appInfo, data.compatInfo);
// (Application) cl.loadClass(className).newInstance();
// app.attachBaseContext()
// app.onCreate()
Application app = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);
mInitialApplication = app;
}
启动主Activity
ActivityStackSupervisor.java:
boolean attachApplicationLocked(ProcessRecord app){
realStartActivityLocked(app);
}
final boolean realStartActivityLocked(app){
app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(intent);
}
App进程由scheduleLaunchActivity经过Handler调用handleLaunchActivity方法,开始启动Activity。
第一步:创建Activity对象(ActivityThread.java):
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = appContext.getClassLoader();
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
第二步:创建PhoneWindow对象(Activity.java):
final void attach(...){
mWindow = new PhoneWindow(this, window, activityConfigCallback);
}
第三步:调用onCreate:
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);
此时Activity的生命周期方法onCreate被调用,接下来是加载Views。
加载Views
Activity的onCreate方法中调用:
public void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID) {
getWindow().setContentView(layoutResID);
initWindowDecorActionBar();
}
PhoneWindow.java:
@Override
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
// Note: FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS may be set in the process of installing the window
// decor, when theme attributes and the like are crystalized. Do not check the feature
// before this happens.
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();
}
mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent);
}
Activity.java:
public void handleResumeActivity() {
// decor = DecorView
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
// wm = WindowManagerImpl
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
// a = Activity
a.mDecor = decor;
a.mWindowAdded = true;
wm.addView(decor, l);
}
WindowManagerImpl.java
@Override
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mContext.getDisplay(), mParentWindow);
}
WindowManagerGlobal.java
// view = DecorView
// parentWindow = PhoneWindow
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow) {
final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams) params;
ViewRootImpl root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
// ArrayList<View> mViews
mViews.add(view);
// ArrayList<ViewRootImpl> mRoots
mRoots.add(root);
// ArrayList<WindowManager.LayoutParams> mParams
mParams.add(wparams);
// do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);
}
ViewRootImpl.java
// view = DecorView
// panelParentView = null
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
// Schedule the first layout -before- adding to the window
// manager, to make sure we do the relayout before receiving
// any other events from the system.
requestLayout();
mWindowSession.addToDisplay(...);
// view.mParent = ViewRootImpl
view.assignParent(this);
}
mWindowSession为:
public final class WindowManagerGlobal {
public static IWindowSession getWindowSession() {
synchronized (WindowManagerGlobal.class) {
if (sWindowSession == null) {
try {
InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.getInstance();
IWindowManager windowManager = getWindowManagerService();
sWindowSession = windowManager.openSession(
new IWindowSessionCallback.Stub() {
@Override
public void onAnimatorScaleChanged(float scale) {
ValueAnimator.setDurationScale(scale);
}
},
imm.getClient(), imm.getInputContext());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
return sWindowSession;
}
}
}
addToDisplay最后调用了:
public class WindowManagerService extends IWindowManager.Stub
implements Watchdog.Monitor, WindowManagerPolicy.WindowManagerFuncs {
public int addWindow(...) {
}
}